45 dna structure with labels
The Structure and Function of DNA - Molecular Biology of the Cell ... The Structure and Function of DNA. Biologists in the 1940s had difficulty in accepting DNA as the genetic material because of the apparent simplicity of its chemistry. DNA was known to be a long polymer composed of only four types of subunits, which resemble one another chemically. Early in the 1950s, DNA was first examined by x-ray diffraction ... The Biology Project The Biology Project, an interactive online resource for learning biology developed at The University of Arizona. The Biology Project is fun, richly illustrated, and tested on 1000s of students. It has been designed for biology students at the college and high school level, but is useful for medical students, physicians, science writers, and all types of interested people.
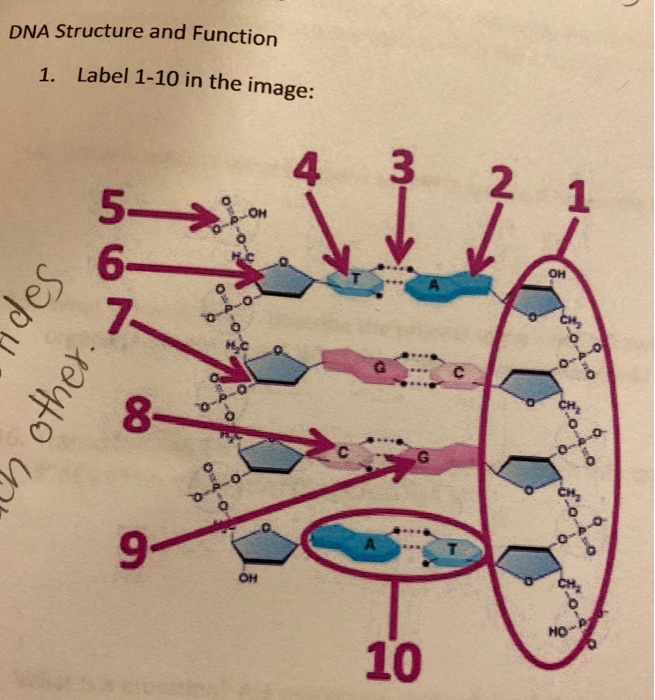
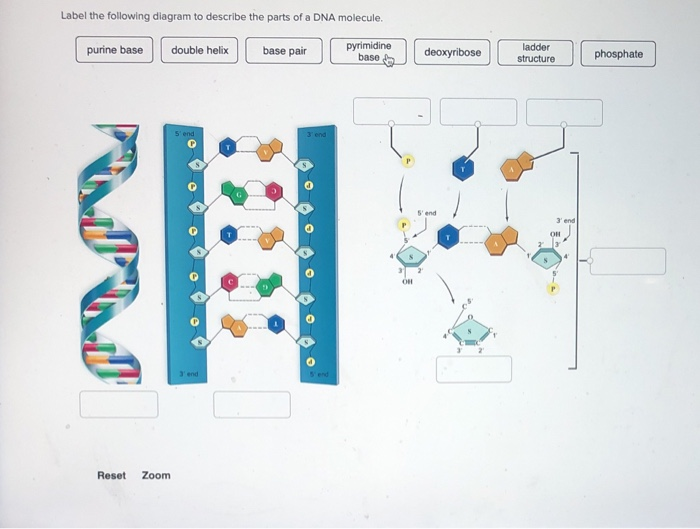
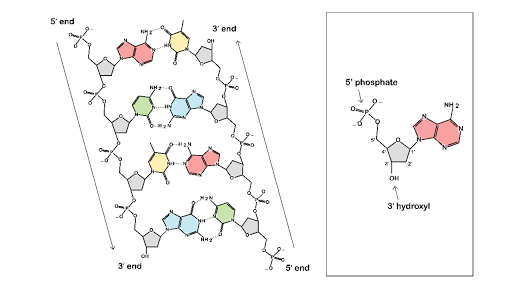
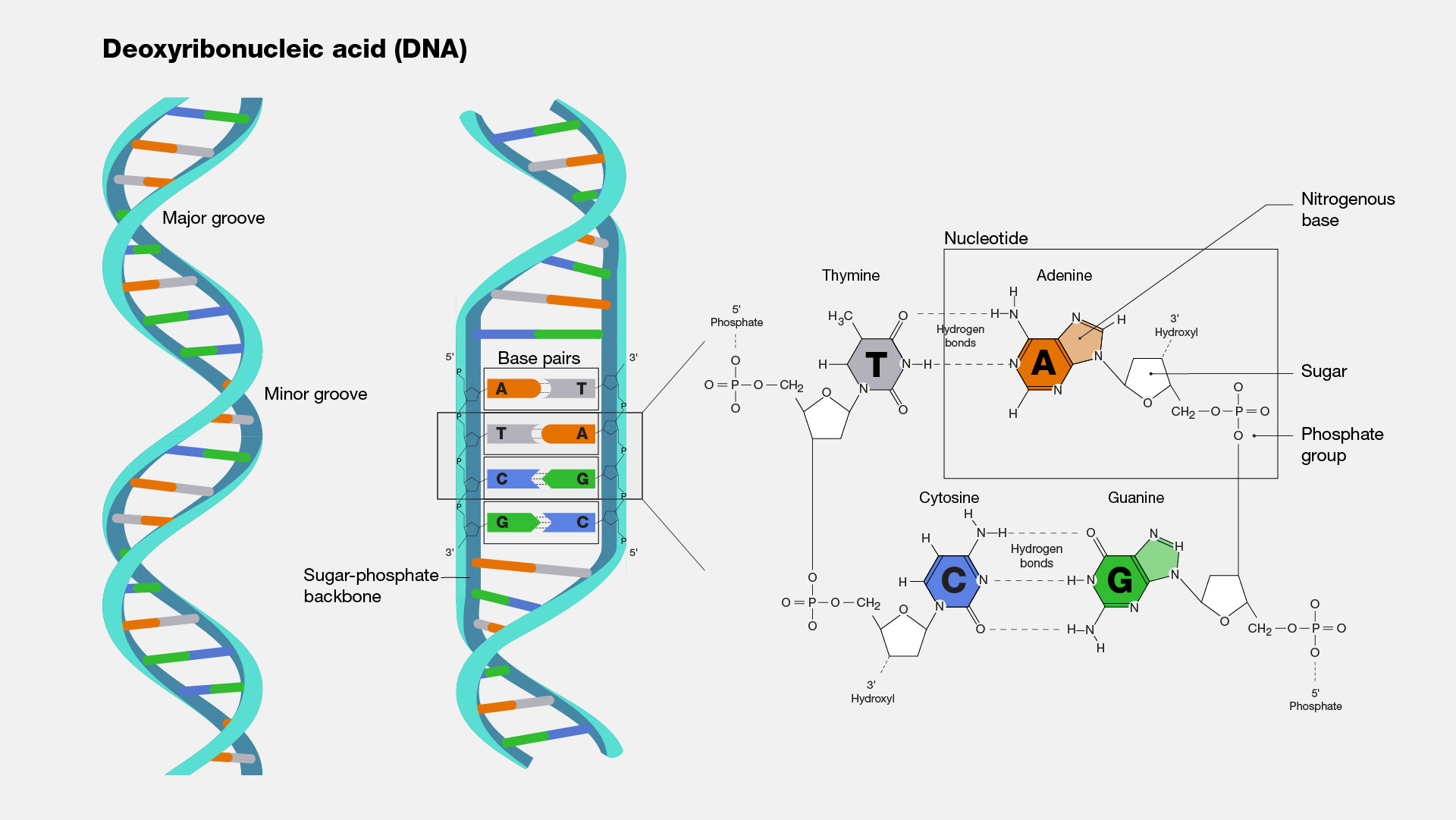
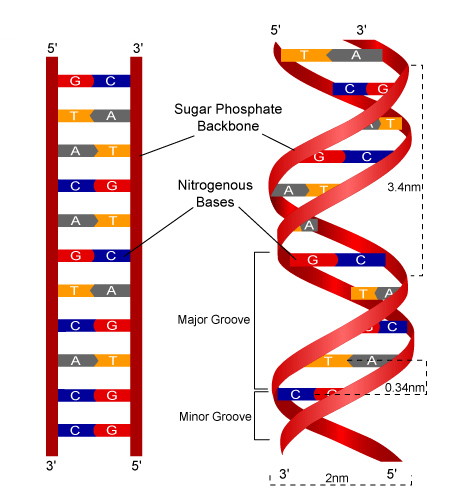
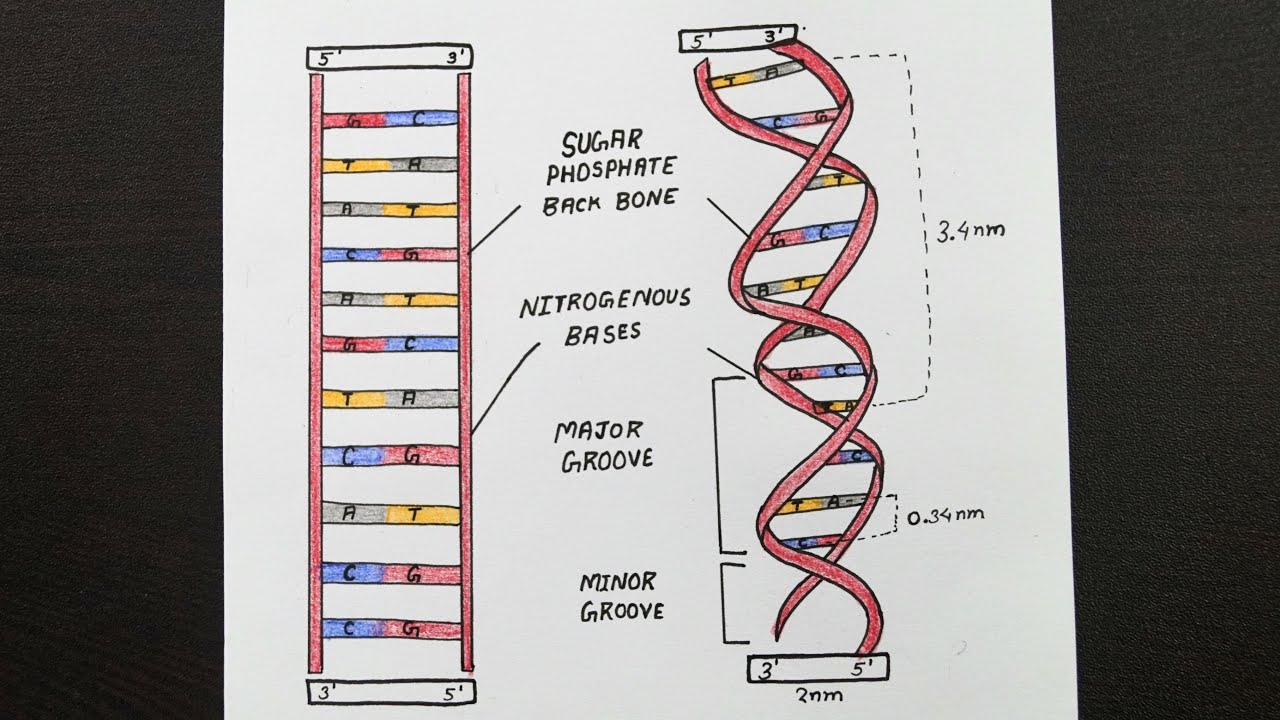
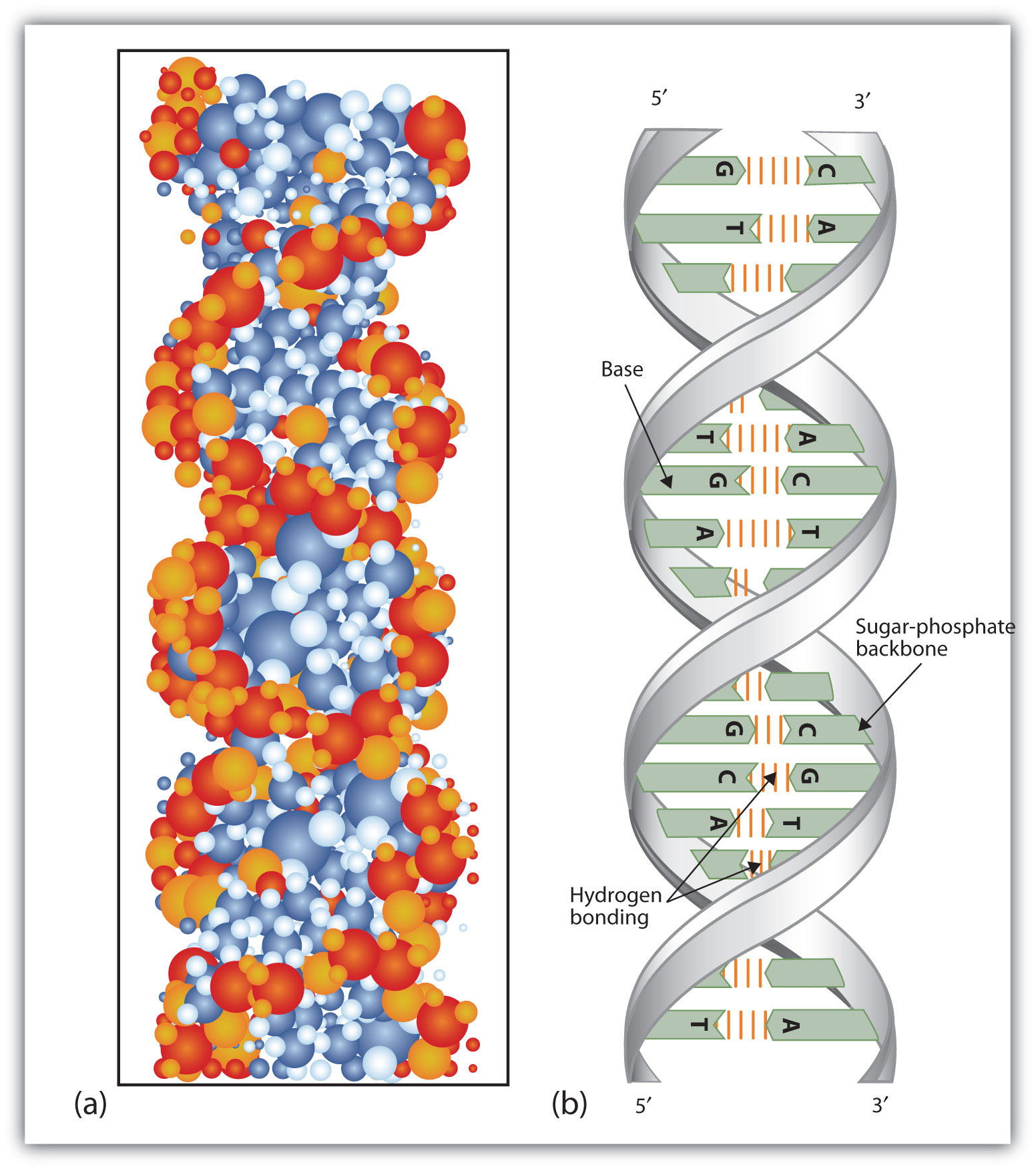
DNA Structure - McGraw Hill Education 4. Doubled-stranded DNA consists of two antiparallel strands, meaning that one strand is oriented in the 5' to 3' direction, while the other is oriented in the 3' to 5' direction. 5. Asymmetrical spacing of the backbones of the DNA double helix generates major and minor grooves.

Dna structure with labels
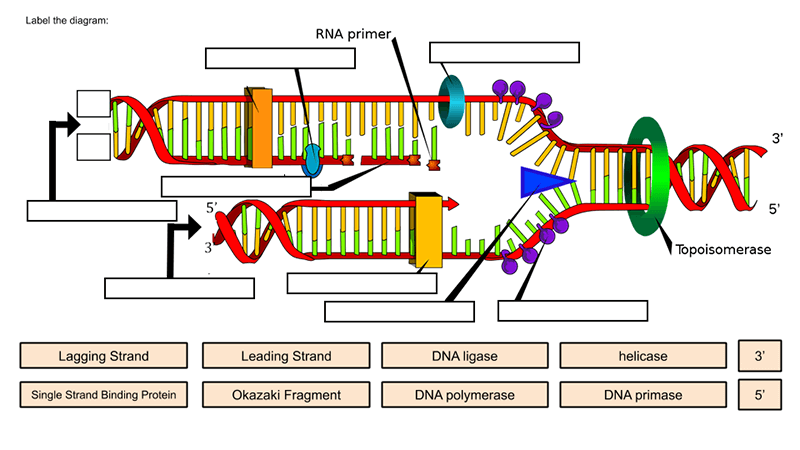
9.1 The Structure of DNA - Concepts of Biology - 1st Canadian Edition A DNA molecule is composed of two strands. Each strand is composed of nucleotides bonded together covalently between the phosphate group of one and the deoxyribose sugar of the next. From this backbone extend the bases. The bases of one strand bond to the bases of the second strand with hydrogen bonds. DNA ligase - Wikipedia DNA ligase is a specific type of enzyme, a ligase, (EC 6.5.1.1) that facilitates the joining of DNA strands together by catalyzing the formation of a phosphodiester bond.It plays a role in repairing single-strand breaks in duplex DNA in living organisms, but some forms (such as DNA ligase IV) may specifically repair double-strand breaks (i.e. a break in both complementary strands of DNA). Barcode Labels and Tags | Zebra Specialty Synthetic Labels For Specialized Applications. Synthetic labels featuring unique facestocks and adhesives to meet the unique requirements of specialized applications. Label features include tamper-evidency, resistance to extreme temperatures and wet surfaces, electro-static dissipative, long-range scanning and many more.
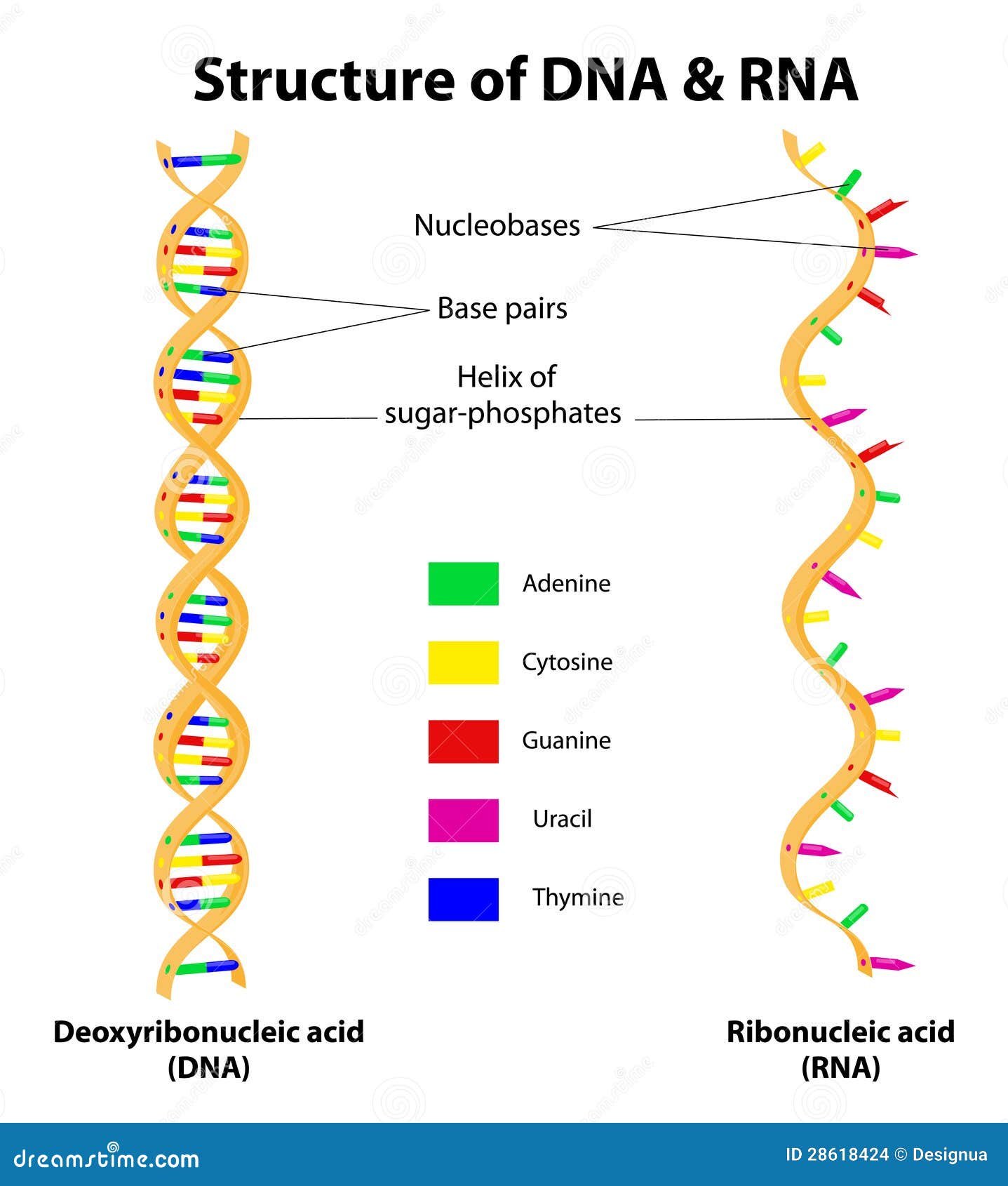
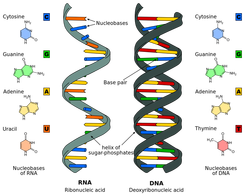
Dna structure with labels. DNA - Wikipedia The structure of DNA is dynamic along its length, being capable of coiling into tight loops and other shapes. In all species it is composed of two helical chains, bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. Both chains are coiled around the same axis, and have the same pitch of 34 ångströms (3.4 nm DNA Structure with Labels - Rae Rocks Teaching Help your students finally understand DNA structure with labels to help them along the way. Nearly 65% of people are visual learners which make graphics key to engaging students. This no-prep lesson provides all the basics you need to provide students to grasp the structure of DNA. $ 4.99, Add to cart, DNA Structure with Labels, Interactive Bacteria Cell Model - CELLS alive Bacteria (Prokaryotes) are simple in structure, with no recognizable organelles. They have an outer cell wall that gives them shape. Just under the rigid cell wall is the more fluid cell membrane. The cytoplasm enclosed within the cell membrane does not exhibit much structure when viewed by electron microscopy. Nucleotide Structure: DNA Diagram | Science Trends DNA has thymine and cytosine as it pyrimidine bases, while RNA has cytosine and a different substance called uracil as its pyrimidine basis. The structure of DNA and RNA is also different. DNA is known for its double helix structure. The double helix is two strands that are intertwined with one another thanks to the complementary bases.
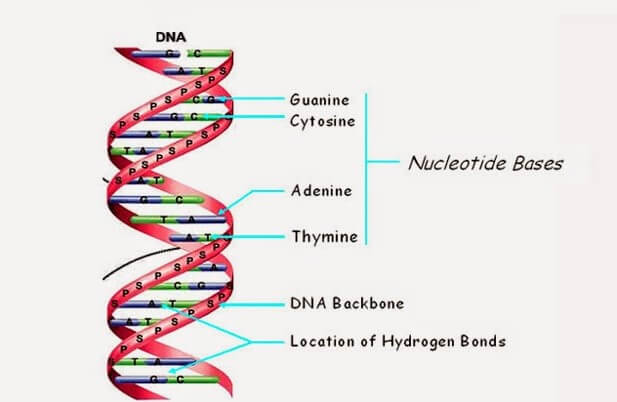
DNA Structure | Biology Dictionary What is the Structure of DNA? DNA molecules are polymers, which means they are large molecules made up of many smaller molecules. The small molecules that make up DNA are called nucleotides. Each nucleotide contains a phosphate group, a sugar molecule (called deoxyribose ), and a nitrogenous base. A nucleotide, The DNA Structure Model - A History of the Double Helix The discovery of the double helix structure of DNA is most often attributed to James Watson and Francis Crick. Using Chargaff's rules and the works of English scientists Rosaline Franklin and Maurice Wilkins, they built a 3D model of the double-helical structure of DNA. American geneticist Maclyn McCarty with Francis Crick and James D. Watson. DNA Structure - YouTube Learn about the structure of DNA and how to recognize all the parts in this video! 11,329 Dna label Images, Stock Photos & Vectors | Shutterstock Genes vector illustration. Educational labeled structure example scheme. Adenine, sytosine, thumine and. Gene ...
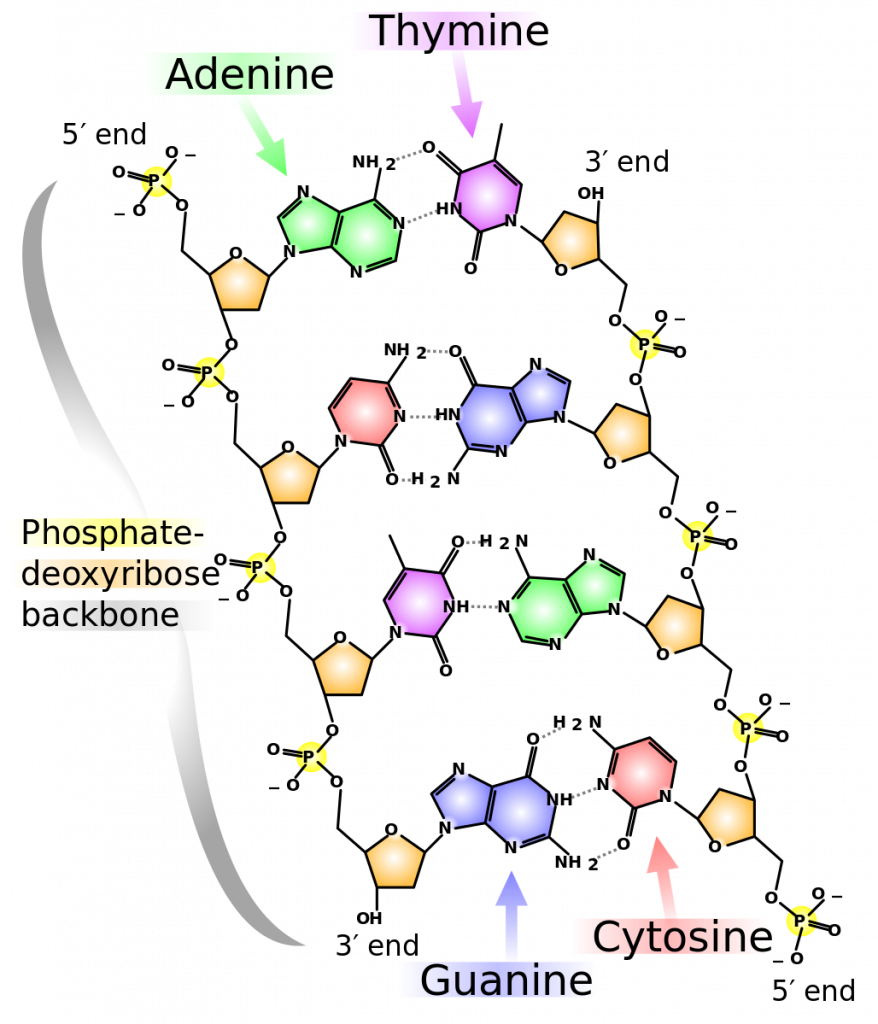
Barcode Labels and Tags | Zebra Specialty Synthetic Labels For Specialized Applications. Synthetic labels featuring unique facestocks and adhesives to meet the unique requirements of specialized applications. Label features include tamper-evidency, resistance to extreme temperatures and wet surfaces, electro-static dissipative, long-range scanning and many more. DNA Structure - Visible Body DNA, A molecule of DNA has two strands, composed of nucleotides, that form a double helix shape. 2. Each DNA strand is composed of nucleotides—units made up of a sugar (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. Each strand of DNA is a polynucleotide composed of units called nucleotides. Labelled Diagram Of DNA Structure || Class 12 || Biology - Pinterest Feb 25, 2020 - Hello Everyone.Diagram Of A DNA Structure || Labelled Diagram Of DNA Structure || Class 12 || BiologyDiagram Of A DNA Structure, ... The Chemical Structure of DNA - Compound Interest The double helix model of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) consists of two intertwined strands. These strands are made up of nucleotides, which themselves consist of three component parts: a sugar group, a phosphate group, and a base. The sugar and phosphate groups combined form the repeating 'backbone' of the DNA strands.
Three's a crowd – stabilisation, structure, and applications ... Aug 24, 2022 · DNA is a strikingly flexible molecule and can form a variety of secondary structures, including the triple helix, which is the subject of this review. The DNA triplex may be formed naturally, during homologous recombination, or can be formed by the introduction of a synthetic triplex forming oligonucleotide (TFO) to a DNA duplex.
DNA Structure - University of Arizona DNA Structure Activity. If you haven't already done so, open the file named "DNA.mcm" with either MacMolecule2 (MacOS) or PCMolecule2 (Windows) molecular visualization software (If need be return to the Introduction for instructions).
Methods for Labeling Nucleic Acids | Thermo Fisher Scientific - FR Nucleic acids may be modified with tags that enable detection or purification. The resulting nucleic acid probes can be used to identify or recover other ...
DNA Structure Labeling Activity Quiz - PurposeGames.com Kidney Labeling Activity 13p Image Quiz. DNA Structure Labeling Activity (Honors) 10p Image Quiz. Spinal Cord Anatomy 10p Image Quiz. Nephron Labeling Activity 9p Image Quiz. Body Region Terminology 50p Image Quiz. Bone Anatomy Labeling Exercise 14p Image Quiz. Internal Brain Anatomy 16p Image Quiz. Urinary System Labeling Practice 9p Image Quiz.
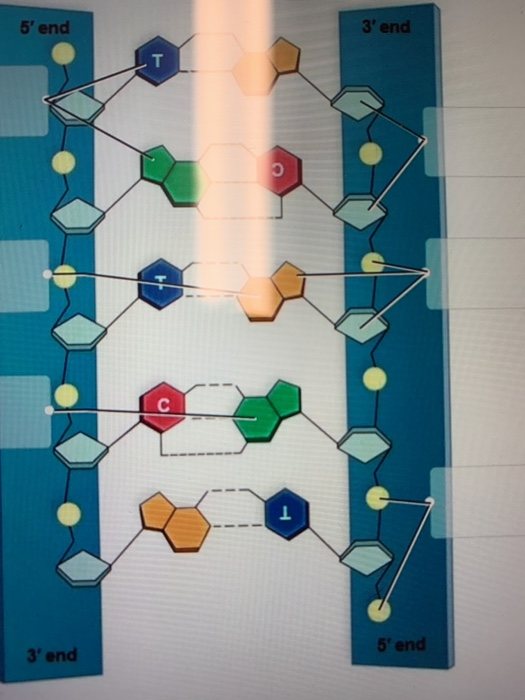
What Is DNA?- Meaning, DNA Types, Structure and Functions - BYJUS The DNA molecule consists of 4 nitrogen bases, namely adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C) and Guanine (G), which ultimately form the structure of a nucleotide. The A and G are purines, and the C and T are pyrimidines. The two strands of DNA run in opposite directions.
DNA: Structure, Forms and Functions (With Diagram) - Biology Discussion DNA contains β D 2′-deoxyribose sugar. It is a five-carbon sugar; hence it is a pentose sugar. Since one oxygen atom at the 2′ carbon is missing it get its name 2′-deoxy. The 2′- deoxy-containing backbone is more resistant to hydrolysis than the riboform. D-ribose does not mean dextrorotary ribose.
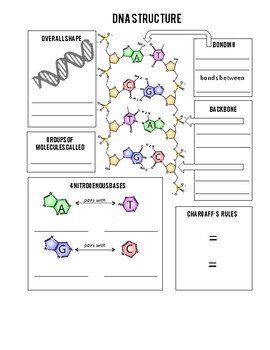
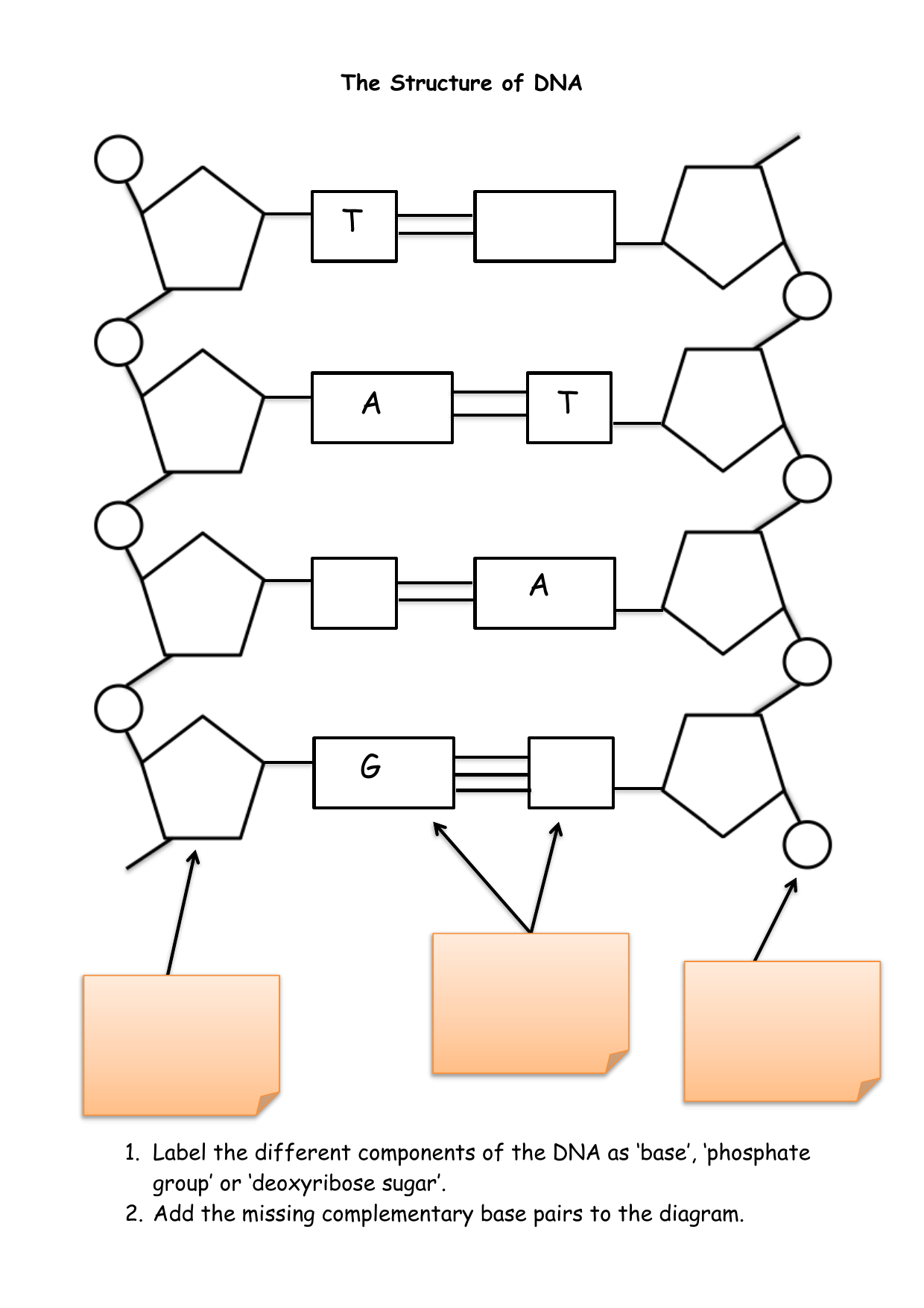
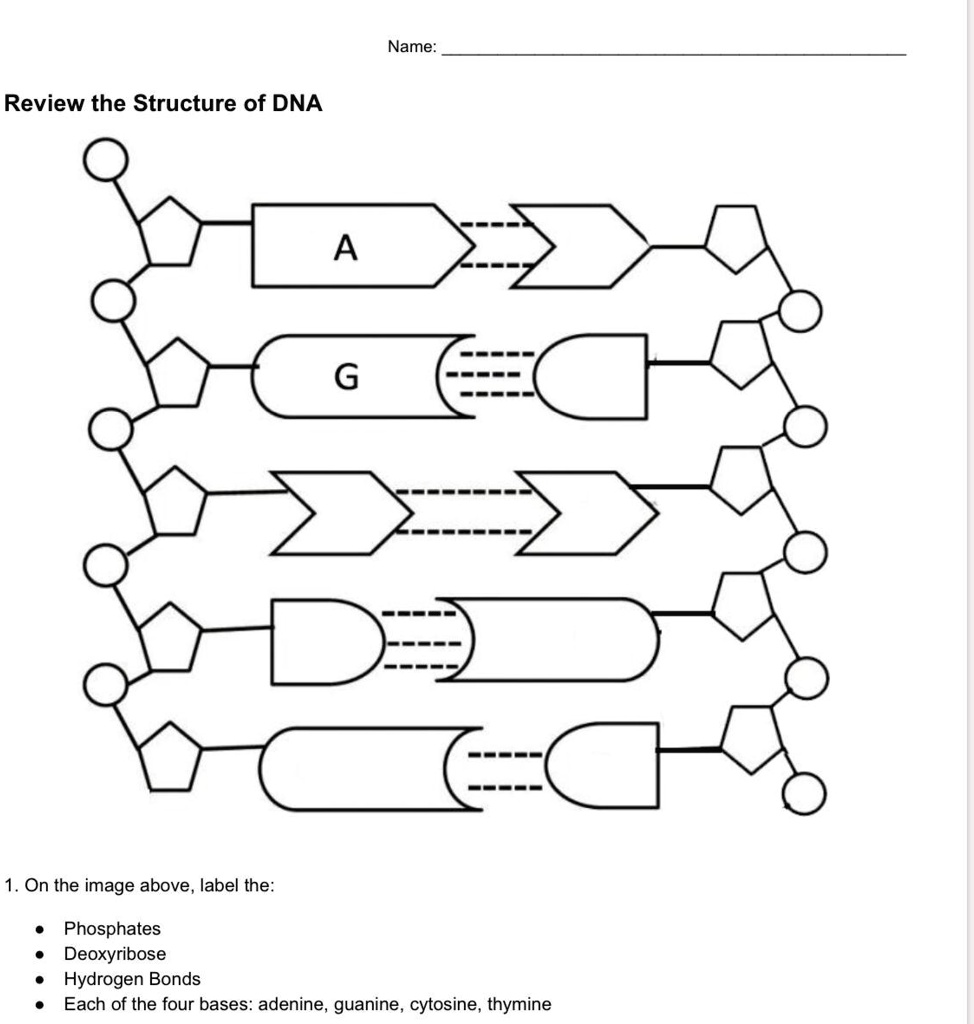
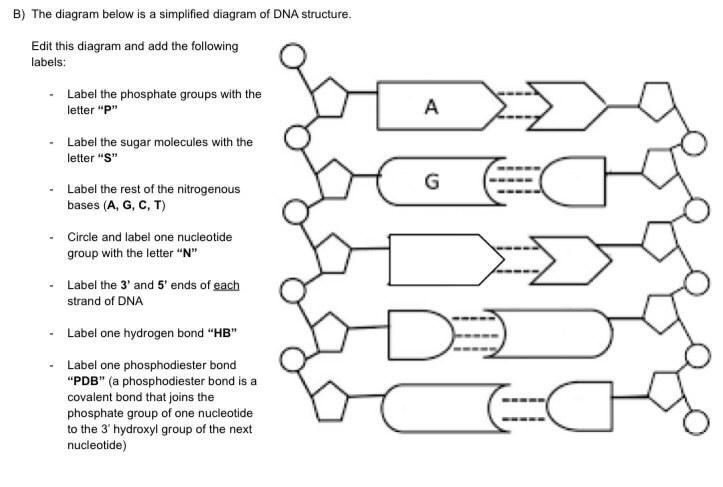
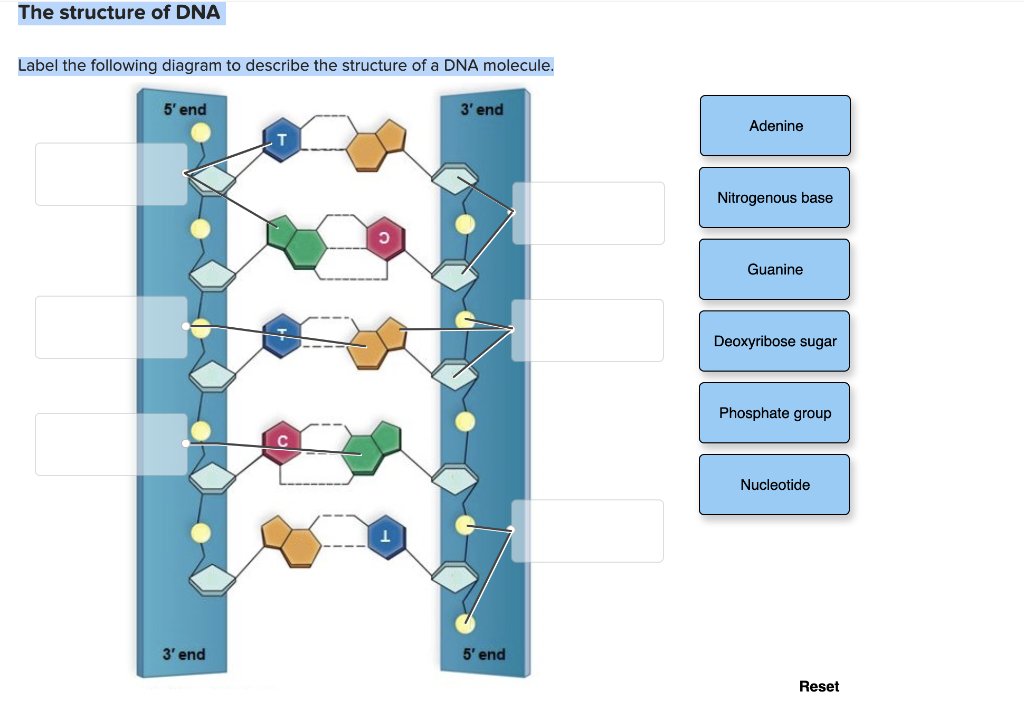
PDF DNA Structure Worksheet - Commack Schools DNA is a polymer, which means that is made up of many repeating single units (monomers). What are the monomers called? 3. The "backbone" of the DNA molecule is made up of two alternating components, what are these? 4. There are four different variations of these monomers (four different bases), what are the names of those bases? 5.
DNA Structure & Function: A Simple Guide - Human Origin Project DNA molecules arrange themselves in a model called the DNA double helix. It's a 3-D structure that is stored in the nucleus of all cells. Remember that the phosphate and sugar molecules are the backbones of the ladder. The bases (A, G, C, G) form the rungs of the ladder. The two-sided ladder formation of the double-helix DNA structure. Source,
Structure Of DNA | Function, Summary, Diagram & Model - A Level Biology DNA is made of two polynucleotide chains, DNA is a polymer of nucleotides. These nucleotides are arranged in the form of two chains. The nucleotides present in DNA are deoxyribonucleotides. They are made up of, Deoxyribose sugar, A nitrogenous base, One phosphate group, One of the following four bases is present in DNA nucleotides. Alanine,
DNA - structure - chemguide In DNA, these bases are cytosine (C), thymine (T), adenine (A) and guanine (G). Note: These are called "bases" because that is exactly what they are in chemical terms. They have lone pairs on nitrogens and so can act as electron pair donors (or accept hydrogen ions, if you prefer the simpler definition).
DNA ligase - Wikipedia DNA ligase is a specific type of enzyme, a ligase, (EC 6.5.1.1) that facilitates the joining of DNA strands together by catalyzing the formation of a phosphodiester bond.It plays a role in repairing single-strand breaks in duplex DNA in living organisms, but some forms (such as DNA ligase IV) may specifically repair double-strand breaks (i.e. a break in both complementary strands of …
Dna Model: Types of DNA, Levels, Structure, Diagram - Embibe This article covers the structure of DNA, types of DNA, etc. To know more about the DNA Model, scroll down the article. What is DNA? DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is the largest macromolecule or biopolymer that is made up of small monomeric units called nucleotides joined by phosphodiester bonds. DNA carries the genetic instructions for the ...
DNA Molecule Label Diagram | Quizlet A pair of complementary nitrogenous bases in a DNA molecule, Hydrogen Bonds, Bond holding together Nitrogen Bases in DNA, Sugar-Phosphate Backbone, The alternating chain of sugar and phosphate to which the DNA and RNA nitrogenous bases are attached, DNA Molecule, Very long and is made up of hundreds of thousands of genes, Sets with similar terms,
DNA and RNA Structures - CliffsNotes DNA structure. The Watson‐Crick base‐pairing of the two strands largely determines the secondary structure of DNA. All naturally occurring DNAs are double‐stranded, for at least some of their lifetimes. Double‐stranded DNA is a fairly uniform structure, and the need for a regular structure is one way in which changes in DNA (genetic ...
Structure of DNA - Higher Biology Revision - BBC Bitesize DNA structure, DNA is the molecule that holds the instructions for growth and development in every living thing. Its structure is described as a double-stranded helix held together by complementary...
PDF DNA Structure: A-, B- and Z-DNA Helix Families - Boston University structure is known as B-DNA, and represents an average conformation of DNA, based on fibre diffraction studies. However, this average shape of DNA is very unlikely to exist within the cells of living organisms, for several reasons. First, there is simply not enough room for the DNA to be stretched out in a perfect, linear B-DNA conformation.
DNA - Wikipedia DNA is a long polymer made from repeating units called nucleotides, each of which is usually symbolized by a single letter: either A, T, C, or G. The structure of DNA is dynamic along its length, being capable of coiling into tight loops and other shapes. In all species it is composed of two helical chains, bound to each other by hydrogen bonds.
DNA Structure The structure of DNA is a double helix. In other words, it is a double stranded molecule that twists like a spiral staircase. The outsides of the molecule, the ...
Sanger Sequencing Steps & Method - Sigma-Aldrich Sanger sequencing, also known as the “chain termination method”, is a method for determining the nucleotide sequence of DNA. The method was developed by two time Nobel Laureate Frederick Sanger and his colleagues in 1977, hence the name the Sanger Sequence. To review the general structure of DNA, please see Figure 2.
Labelled Diagram Of DNA Structure || Class 12 || Biology - YouTube Feb 23, 2020 ... Hello Everyone.Diagram Of A DNA Structure || Labelled Diagram Of DNA Structure || Class 12 || BiologyDiagram Of A DNA Structure, ...
3.3.5 Draw a simple diagram of DNA structure - YouTube Here I demonstrate drawing the structure of DNA. You don't need to be an artist, its relative positions of the phosphate groups, deoxyribose sugar (together known as the sugar-phosphate backbone),...
How to Label a DNA Structure - Sciencing Apr 24, 2017 ... A DNA strand is made of four bases, classified with the letters A, C, T, and G. A stands for adenine (a purine); C stands for cytosine (a ...
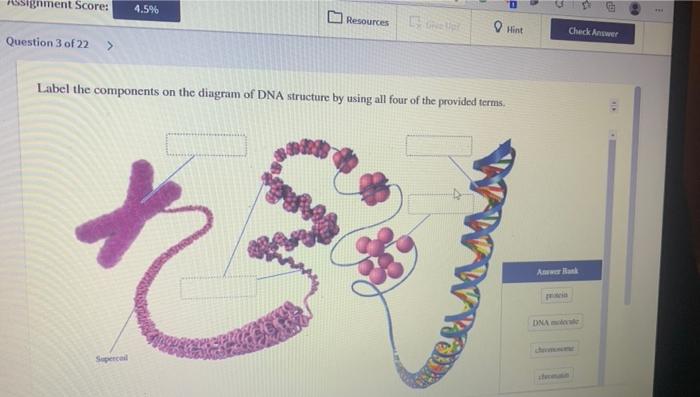
DNA function & structure (with diagram) (article) | Khan Academy DNA is the information molecule. It stores instructions for making other large molecules, called proteins. These instructions are stored inside each of your cells, distributed among 46 long structures called chromosomes. These chromosomes are made up of thousands of shorter segments of DNA, called genes.
DNA Structure Labeling Diagram | Quizlet the spiral-staircase structure characteristic of the DNA molecule, nitrogen base, a subunit of a nucleotide in DNA and RNA, pyrimidine, a nitrogen base that has a single-ring structure (thymine, cytosine, and uracil) purine, a nitrogen base that has a double-ring structure (adenine and guanine) thymine, pairs with adenine, adenine,
Three's a crowd – stabilisation, structure, and applications of DNA ... 24/08/2022 · This structure has been widely characterised by X-ray diffraction and occurs at high humidity and with a variety of DNA counterions including Na +, which serves to balance the negative charge of the phosphate backbone. 3,4 The most significant characteristic of B-DNA is the possibility to accommodate only two types of naturally occurring base pairs (i.e., …
The Structure of DNA - University of Arizona The Structure of DNA, Nucleic acids are made up of chains of many repeating units called nucleotides (see bottom left of Figure 1 below). The DNA molecule actually consists of two such chains that spiral around an imaginary axis to form a double helix (spiral.)
Pfam: Family: Put_DNA-bind_N (PF06971) Putative DNA-binding protein N-terminus Provide feedback. This family represents the N-terminus (approximately 50 residues) of a number of putative bacterial DNA-binding proteins. Internal database links . SCOOP: GntR HrcA_DNA-bdg HTH_11 HTH_20 HTH_24 HTH_DeoR HTH_PafC MarR MarR_2 Rrf2: Similarity to PfamA using HHSearch: HTH_DeoR HTH_11: External …
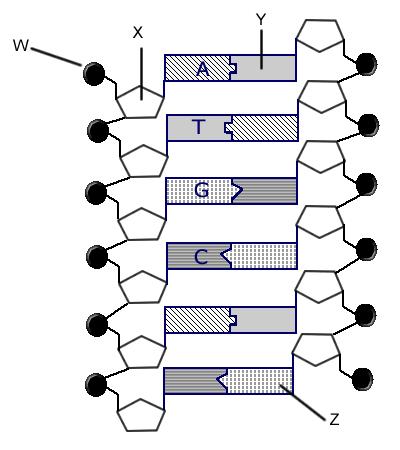
Review the Structure of DNA - The Biology Corner On the image above, label: Phosphate. Deoxyribose. Hydrogen Bonds. Each of the four bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine. 2. The process by which DNA ...
dna-labeling | NEB A variety of enzymatic or chemical methods are available to generate nucleic acids labeled with radioactive phosphates, fluorophores, or nucleotides modified with biotin or digoxygenin for example. Nucleic acids may be labeled at their 5´ end, their 3´ end, or throughout the molecule depending on the application.
Barcode Labels and Tags | Zebra Specialty Synthetic Labels For Specialized Applications. Synthetic labels featuring unique facestocks and adhesives to meet the unique requirements of specialized applications. Label features include tamper-evidency, resistance to extreme temperatures and wet surfaces, electro-static dissipative, long-range scanning and many more.
DNA ligase - Wikipedia DNA ligase is a specific type of enzyme, a ligase, (EC 6.5.1.1) that facilitates the joining of DNA strands together by catalyzing the formation of a phosphodiester bond.It plays a role in repairing single-strand breaks in duplex DNA in living organisms, but some forms (such as DNA ligase IV) may specifically repair double-strand breaks (i.e. a break in both complementary strands of DNA).
9.1 The Structure of DNA - Concepts of Biology - 1st Canadian Edition A DNA molecule is composed of two strands. Each strand is composed of nucleotides bonded together covalently between the phosphate group of one and the deoxyribose sugar of the next. From this backbone extend the bases. The bases of one strand bond to the bases of the second strand with hydrogen bonds.





















Post a Comment for "45 dna structure with labels"